How Does Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) Relate to Data Governance?
Seth Knox
As organizations expand across cloud, SaaS, and hybrid environments, security and compliance leaders are flooded with acronyms and new tools. Data Security Posture Management (DSPM), Data Security Governance (DSG), and Data Access Governance (DAG) are among the most important emerging categories—but how do they work together?
Veridian Credit Union offers a great example of this journey in action. After implementing LightBeam, their team noted: “We came to LightBeam for classification, but we’re already thinking about how to build a more strategic data governance program.” Read the full case study.
This blog explains how DSPM fits within the broader data governance ecosystem and how organizations can operationalize these frameworks to reduce risk and drive business outcomes.

Understanding Your Data Security Maturity
Understanding where your organization stands in its data security journey is essential before adopting new tools or strategies. Most organizations fall into one of three stages: Foundational, Expanding, or Optimizing. At the Foundational stage, teams often have limited visibility into where sensitive data lives, lack consistent policies, and respond reactively to incidents rather than proactively managing risk. The Expanding stage reflects a growing recognition of regulatory requirements, with teams beginning to invest in privacy tools and automated controls. In the Optimizing stage, organizations aim for deep integration across their security stack, clear accountability, and alignment with business objectives.
Progressing through these stages requires not just better tools, but better alignment across stakeholders.
What Is Data Security Governance (DSG)?
Data Security Governance (DSG) is the strategic framework that defines how organizations evaluate, manage, and prioritize data-related risks. Unlike purely technical controls, DSG requires business alignment—ensuring that policies around data access, retention, and classification serve both security goals and operational needs.
DSG helps stakeholders define acceptable levels of risk, codify policies for sensitive data, and align governance requirements with industry regulations. It creates the foundation upon which DSPM and DAG tools operate, offering the context and control necessary to guide automated enforcement and remediation activities. When implemented effectively, DSG becomes the connective tissue that ensures security investments translate into measurable business outcomes.
For a deeper dive into how DSPM works and the outcomes it can drive, check out our blog post: What Is Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) and What Can It Do for You?
What Is Data Access Governance (DAG)?
Data Access Governance (DAG) complements DSPM by focusing specifically on who has access to data and whether that access is appropriate based on identity, role, and business context. Gartner defines that DAG “provides assessments for data access, and management and real-time monitoring capabilities for unstructured and semistructured data found in file repositories. Its primary purpose is to determine, manage and monitor who has access to which data in an organization’s repositories and rectify oversharing of data.”. (Gartner®, Hype Cycle™ for Data Security, 2024, 29 July 2024).
Where DSPM provides visibility into the data itself, DAG adds a critical layer of identity-awareness. It connects with identity and access management (IAM) systems, evaluates real-world permissions against governance policies, and helps enforce principles such as least privilege and need-to-know. This is particularly important in regulated industries, where over-entitled users or outdated access paths can lead to compliance violations and increased breach risk.
Together, DAG and DSPM create a feedback loop: DSPM discovers and classifies sensitive data and flags risk, while DAG ensures that only the right users have access to that data under the right circumstances. Combined with DSG, these tools form a unified framework for visibility, control, and accountability in data security programs.
Visualizing the Relationship Between DSG, DSPM, and DAG
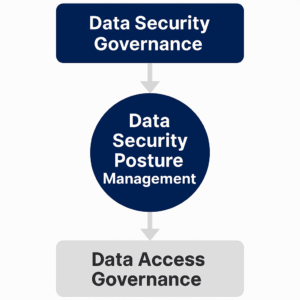
Imagine a horizontal flow: at the leftmost point, Data Security Governance (DSG) defines the business-aligned rules, policies, and risk tolerance thresholds. These policies then guide the operational layer, where DSPM continuously discovers data, evaluates posture, and surfaces exposures. On the right, DAG validates access paths against policies to ensure only authorized individuals can interact with sensitive data. Each layer informs and reinforces the others in a cycle of governance, detection, and enforcement.
This visualization helps illustrate how these three concepts are not competing solutions but interdependent components of a mature data security framework. Without DSG, efforts lack direction; without DSPM, they lack visibility; and without DAG, they lack enforcement.
Aligning Stakeholders Across the Organization
Effective data governance and security cannot be achieved by the IT department alone. It requires a coalition of leaders from security, data, privacy, and operations to establish goals, approve policies, and maintain ongoing accountability. A common way of moving data governance and security forward is by putting together a Data Security Steering Committee composed of roles like Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), Chief Data Office (CDO), Chief Privacy Officer (CPO), and Chief Information Office (CIO).
Each of these roles brings a unique perspective: the CISO ensures that security measures are aligned to risk mitigation; the CDO or CDAO ensures that data strategy supports business agility; the CPO ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA; and the CIO ensures technical feasibility and integration across the organization. By working together, they can prioritize initiatives, review posture reports, and align their teams around a common data risk framework.
How LightBeam Unifies DSPM and Governance with Identity-Centric Intelligence
LightBeam.ai is purpose-built to help organizations operationalize Data Security Posture Management (DSPM), Data Security Governance (DSG), and Data Access Governance (DAG) by bridging the gaps between key stakeholders: CISOs, CDOs, CPOs, and CIOs. At the center of this capability is the AI-powered Data Identity Graph, which unifies visibility into sensitive data with identity and business context across environments. Unlike traditional scanning tools, LightBeam performs deep, full-content analysis of every document—ensuring precise and reliable classification at scale.
CISOs benefit from LightBeam’s risk-driven approach, using it to detect exposures, monitor access behavior, and implement automated remediation that aligns with overall security posture. CDOs and CDAOs gain from the platform’s ability to tie data assets to business value and risk, supporting strategic data initiatives and compliance alignment. For CPOs and compliance leaders, LightBeam automates discovery and labeling of regulated data while automating common privacy operations such as Data Subject Requests, Privacy Impact Assessments, and Consent management. And CIOs find value in LightBeam’s seamless integration with existing IT and security infrastructure, accelerating deployment and minimizing friction.
LightBeam enables enforcement of policies defined through DSG with powerful remediation capabilities. These include the ability to automatically revoke access to sensitive data, redact confidential information, archive unnecessary copies, or delete data in violation of retention policies. This automation streamlines incident response and lowers the burden on overworked security teams.
One of LightBeam’s standout capabilities is Privacy at Partners, which gives organizations visibility into how sensitive data is shared externally. This is critical for evaluating third-party risk. For example, when an employee shares customer data with a business partner, LightBeam can determine whether that sharing aligns with internal DSG policies or constitutes a policy violation. This insight allows teams to intervene when necessary and build trust when appropriate.
By connecting data to people and policies with complete transparency, LightBeam helps data security leaders align governance, security, and IT functions. It becomes the central platform that brings together all stakeholders—technical and non-technical—to make informed decisions about how sensitive data should be handled, protected, and used.
Customers also benefit from features such as real-time data maps, automated labeling and retention enforcement, and integrated regulatory reporting. LightBeam helps teams move from reactive compliance to proactive governance by merging the best of DSPM, DAG, and DSG in one intelligent, unified platform. It provides the foundation to understand not just where data is, but who it belongs to, who can access it, and what should happen to it next.
Final Thoughts
To effectively manage sensitive data and meet privacy regulations, don’t start by buying more tools. Instead, begin with a data security strategy and risk assessment that aligns stakeholders through a robust data governance framework. From there, use DSPM to operationalize those policies, detect exposure, and surface actionable risks. DAG then enforces identity-aware access controls that ensure data is only available to the right people, in the right context. With LightBeam, you can unify these domains into one intelligent, scalable solution for data protection.
GARTNER and HYPE CYCLE are registered trademarks of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in
the U.S. and internationally and are used herein with permission. All rights reserved.
FAQ Section
Q1. What is the relationship between DSPM and Data Governance?
A: DSPM (Data Security Posture Management) operationalizes the policies set by Data Governance. While Data Governance defines how data should be managed, DSPM ensures continuous monitoring, classification, and protection of that data across environments.
Q2. How does Data Access Governance (DAG) complement DSPM?
A: DAG adds the identity layer to DSPM by controlling who can access which data and why. Together, DSPM identifies risks in data exposure, while DAG enforces least-privilege access policies to prevent oversharing and compliance violations.
Q3. What is the difference between DSPM, DSG, and DAG?
A:
-
DSG (Data Security Governance) defines policies and acceptable risk thresholds.
-
DSPM discovers and classifies data to surface posture and risk.
-
DAG enforces access controls based on identity and business context.
All three work together to deliver continuous visibility, compliance, and control.
Q4. Why is stakeholder alignment critical for data governance?
A: Data security cannot be handled by IT alone. Collaboration between CISOs, CDOs, CPOs, and CIOs ensures that governance frameworks align with business goals, compliance requirements, and security policies.
Q5. How does LightBeam unify DSPM, DAG, and DSG?
A: LightBeam connects sensitive data, identities, and governance policies through its AI-powered Data Identity Graph. It automates discovery, risk scoring, and access enforcement—creating one unified platform for governance, privacy, and security.
Related Posts

5 Essential Data Security Steps Before You Roll Out Microsoft Copilot
Learn More
Navigating the 2025 CPRA and CCPA Amendments
Learn More



