Common Challenges and Mistakes when fulfilling DSRs (Data Subject Requests)
Avoid common mistakes in Data Subject Request (DSR) processing. Learn how to automate, verify, and respond accurately and on time.
Bill Schaumann
Table of Contents
- Missing DSR (Data Subject Request) Time Deadlines
- Incomplete or Inaccurate Responses while filling the Data Subject Request form
- Lack of Identity Verification
- Inadequate Data Discovery for DSR Processing
- Not Handling Structured and Unstructured Data
- Not maintaining audit trails and documentation
- Ignoring Third-Party Data Sharing
- Poor Communication with the Data Subject
- Here is a quick checklist for successful implementation.
- Conclusion
In 2016, the European Parliament and Council of the European Union adopted the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The GDPR became effective in 2018 and quickly challenged the world with new data governance requirements. As an official EU regulation and not merely guidance, as the former EU directive was, the GDPR posed direct legal effect and was supported by serious fines for non-compliance. Chief among these new requirements were articles that outlined new rights given to EU residents and which detailed the activities needed to be taken to respond to requests for access to the personal information being collected, stored, and used by in-scope organizations.
These Data Subject Rights requests or DSRs, challenged organizations to develop new capabilities related to understanding and effectively managing the personal information of their employees, contractors, consumers, and customers. The requirement required the organization to receive the request, verify the requestor, find the appropriate data in an ever-expanding digital environment, and either provide a copy, correct, or delete the requestor’s personal data, all within a pre-determined timeframe.
These GDPR requirements changed the way the world looked at privacy, becoming a model for other global regulations and standardizing the DSR concept across the globe. Although most compliance teams understand these requirements today, not all have successfully implemented the systems and processes needed to seamlessly fulfill the DSRs they have received.
Historically, the ability to catalog all the data a company processes, fully understand why and how the data is being processed and apply consistent operational controls was an unattainable goal only partially existing at the department level. Department heads could describe their processes and the systems being used, but rarely had a view of all the data elements or attributes of their systems. Therefore, finding data of a single requestor is a manual and time consuming task.
As DSR response systems and processes are developed and deployed, there are many common obstacles that will need to be addressed to fulfill a DSR request.

Missing DSR (Data Subject Request) Time Deadlines
Most regulations that require DSRs include a length of time in which the request has to be filled. Generally, the response time requirement is about one month. That is 30 days to receive the request, verify the request type and the requestor’s identity, assemble the appropriate requestor’s data, approve the assembled package, and send it to the requestor. Along the way, communications should be sent to the requestor, updating them on the status of their request. Companies often fail in meeting the time requirement due to using manual tracking processes and not fully understanding the data that is spread and stored in disparate systems.
LightBeams’ automated DSR workflow leverages our identity graph technology to accurately gather, package, and distribute appropriate requestor data to the requestor in pre-designated time frames.
Incomplete or Inaccurate Responses while filling the Data Subject Request form
Most organizations today have data spread across a multitude of systems and repositories that support many business functions. Manually finding all the data of a particular requestor is time consuming and often inaccurate. Understanding which Jane Doe in a client prospecting system goes with another Jane Doe in a Marketing spreadsheet can be a difficult task to complete quickly. The worst error that can be committed in fulfilling DSR requests is to give a requestor someone else’s data.
LightBeam’s automated data discovery and classification system leverages identity graph technology to accurately develop views of a requester’s data needed to support DSR processing.
Lack of Identity Verification
Identity verification can be difficult and arduous if the processes and data identification is incomplete. Failing to verify the identity of a requestor runs the risk of providing the data to the wrong person. In verifying an identity, new data cannot be collected, and sensitive data should not be revealed in communications. Her,e companies can fail to fully understand the role of the requestor and what data has been collected for people in this role.
LightBeams’ automated DSR workflow includes requestor verification steps to provide instant identity verification against already known data. No new data needs to be collected for verification.
Inadequate Data Discovery for DSR Processing
Many companies don’t have tools to locate personal data across all their systems. Relying on manual searches and incomplete inventories leads to both incomplete data and missed due dates. The ability to manually assimilate the bits and pieces of data that compose an identity is an impossible task in large digital environments. Organizations that base DSR processing on manual reviews and determinations of what data is being processed will ultimately fail by having an inaccurate view of the requested data and an incomplete DSR response.
LightBeam’s automated data discovery and classification system leverages identity graph technology to accurately develop views of requestor data. Complete view of the entities, attributes and their repositories is instantly available for every data subject. Always accurate data and process inventory allows for governance enforcement polices to manage the use of personal information.
Not Handling Structured and Unstructured Data
In today’s digital environments, data exists in many forms and in a variety of applications, files, and databases. In addition to the more obvious business transactional and structured databases like Salesforce, Stripe, or PeopleSoft, lots of personal information remains hidden in unstructured data files that exist across the network. Many types of documents and files are stored in network share drives like GDrive and Sharepoint; Enterprise communication apps like email or chat apps like Teams and Slack. And they all can contain personal information. Not including these repositories in data inventory scanning and governance monitoring raises many privacy and security risks. By scanning, classifying, and governing both structured and unstructured data more complete governance and security controls can be implemented.
Connecting any type of data source to LightBeam is quick and easy with API connections. LightBeam can find and assimilate personal information from across both structured and unstructured repositories to locate, analyze, and classify sensitive information.
Not maintaining audit trails and documentation
Many regulations require good documentation on the processing of DSRs. When investigating breaches , many regulators will want to review the records of DSR processing. Manual documentation systems can produce incomplete or inaccurate records. By automating the DSR proces,s accurate DSR processing records are created and maintained automatically.
LightBeam automatically documents every request, requestor communications, and report issued in a permanent archival record, which are always available for easy access.
Ignoring Third-Party Data Sharing
Much of today’s transactional business processes are carried out by third-party vendors, contracted for specific functions. Forgetting to include data shared with processors, vendors, or affiliates can lead to poor DSR execution. Not identifying and coordinating with these parties for access or deletion requests creates incomplete processing of DSR requests.
LightBeams’ automated workflow and data discovery ensure that all data being processed is accounted fo,r including processor data in DSR requests. The LightBeam Privacy at Partners module creates clear observability of the data being shared with outside entities.
Poor Communication with the Data Subject
Manual DSR processing can lead to inconsistent messaging regarding the status of an individual’s DSR requests. Building brand reputation begins with the relationship you maintain with your customers. Building trust in these relationships is accomplished with clear and timely messaging when a DSR request is received.
LightBeams’ automated DSR process provides an automated communications service that leverages predefined and editable messaging templates for every step of the process, ensuring that Data Subjects are informed about the personal information they have shared with your organization.
End-to-end processing of DSR requests requires several steps and activities to be effective.
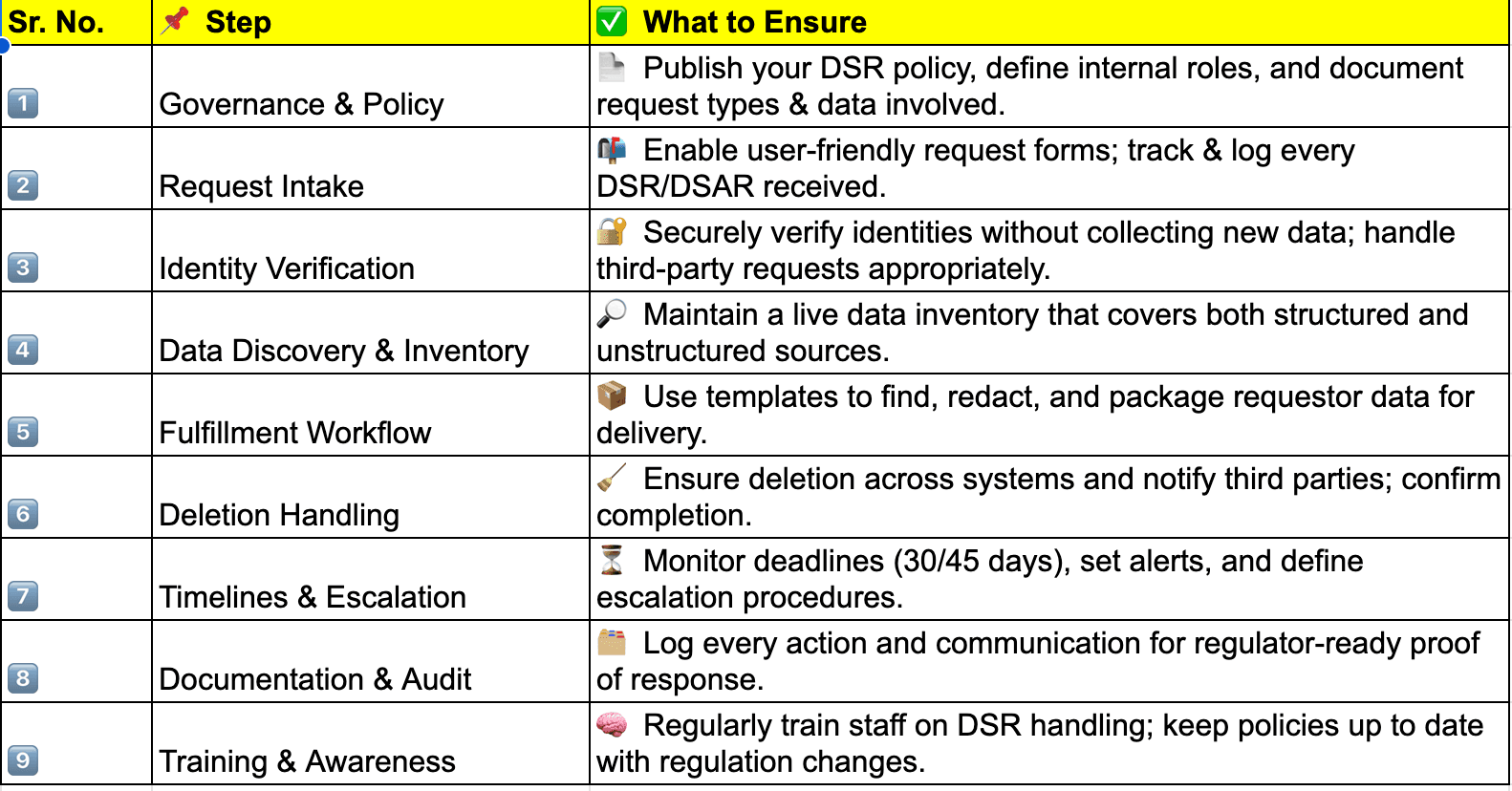
Here is a quick checklist for successful implementation.
💡 Ready to streamline this entire checklist?
See how LightBeam automates every step of DSR processing →
1. Governance & Policy
– Privacy Notice containing DSR policy is documented and publicly available
– Internal roles/responsibilities for DSR processing are clearly defined
– Procedures for different types of requests (access, delete, correct, etc.) have been vetted with legal, and what data is involved has been identified and documented.
2. Request Intake
– User-friendly request forms available (web form, email, phone, etc.) feed into the workflow system.
– Clear guidance to data subjects on what info they previously provided is needed
– A system to track and log each DSR/DSAR
3. Identity Verification
– Process to verify identity securely and proportionately without collecting new information.
– Procedures are in place for handling agent or representative requests
4. Data Discovery & Inventory
– Accurate automated data map or inventory across systems (cloud, on-prem, SaaS)
– Capability to search both structured and unstructured data
– Tools to find sensitive data (PII, PHI, etc.)
5. Fulfillment Workflow
– Create templates for standard responses
– Find relevant requestor data and package for delivery
– Redaction tools for sensitive or third-party data
6. Deletion Handling
– Process to delete from production and backup systems.
– Process to revoke access to the remaining data.
– Process to notify and confirm deletion with third parties/vendors.
7. Timelines & Escalation
– Mechanism to track time limits (30/45 days)
– Alert functions for exceeding the timeline
– Escalation paths for legal or complex requests
8. Documentation & Audit
– Logging of all request activity and actions taken
– Proof of response provided to regulators if needed
9. Training & Awareness
– Staff trained to recognize and respond to DSRs
– The privacy team regularly reviews policy and compliance
Watch how LightBeam automates DSR in action:
Conclusion
Processing DSRs or Data Subject Requests can be a difficult task for any organization, and can become overwhelming when request numbers go up. Automatically processing DSR requests is about enabling growth, trust, and agility. In 2025, it’s the difference between companies that thrive in a data-first world and those left behind.
Fulfilling Data Subject Requests (DSRs) under regulations like GDPR requires accurate data discovery, identity verification, and timely response. LightBeam automates this with end-to-end workflows that reduce risk and ensure compliance.
Ready to move from reactive to strategic DSR processing? Let LightBeam show you how.
Explore how LightBeam’s identity-centric data governance platform can help you discover, secure, and govern your sensitive data across SaaS, cloud, and on-prem environments. Schedule a demo or read a customer story to see the impact firsthand.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is a Data Subject Request (DSR)?
A1: A Data Subject Request (DSR) is a formal request made by an individual to access, correct, delete, or port their personal data held by an organization, as granted under laws like the GDPR, CCPA, and others.
Q2: Why are DSRs challenging for organizations to fulfill?
A2: Organizations struggle with DSRs due to data being siloed across systems, poor identity verification processes, lack of structured workflows, and difficulty handling both structured and unstructured data.
Q3: How can automation help in fulfilling DSRs?
A3: Automated DSR workflows like those from LightBeam use identity graphs and data discovery tools to accurately find, verify, package, and fulfill requests within regulatory deadlines—minimizing human error and increasing efficiency.
Q4: What happens if a DSR is not fulfilled correctly or on time?
A4: Failure to fulfill a DSR can lead to regulatory penalties, loss of customer trust, and legal risks—especially under GDPR and similar laws that mandate strict response timelines.
Related Posts

DSR vs. DSAR: A Guide to Data Subject Requests
Learn More
CFPB Rule 1033: What Financial Institutions Must Know to Stay Compliant
Learn More


